...
Connecting "VT85 / Modbus extension board"
Connecting Modbus sensors using "RS485 to USB adapter"
Description
A virtual "Modbus RTU" sensor is used to read and write data from external equipment via Modbus RTU protocol (RS-485 line). Such equipment can be sensors/meters or devices/systems/units.
...
Fields in the form available for change:
# | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Name | Created element name |
2 | User-defined type | Defines the icon to be displayed in the "System tree" |
3 | Units of measurement | The unit of measure in which the value is displayed in the "System tree" |
4 | Minimum value | Determines the minimum measurement range, when the value is out of range, the sensor goes into "Not connected" state |
5 | Maximum value | Determines the maximum measurement range, when the value is out of range, the sensor goes into a "Not connected" state |
6 | Alarm and warning levels | Defines the alarm and warning thresholds, as for other sensors, see Sensor configuration |
7 | Hysteresis | Option of setting the hysteresis state, see Sensor configuration |
8 | Expression | Function of the form f (x). The default value for the sensor is equal to the measured value: "x", ie corresponds to the expression "x". To calculate the indirect value of the sensor is possible to use an arbitrary expression, which are permissible "(", ")", as well as:
For example: "0.1*x+0.5" |
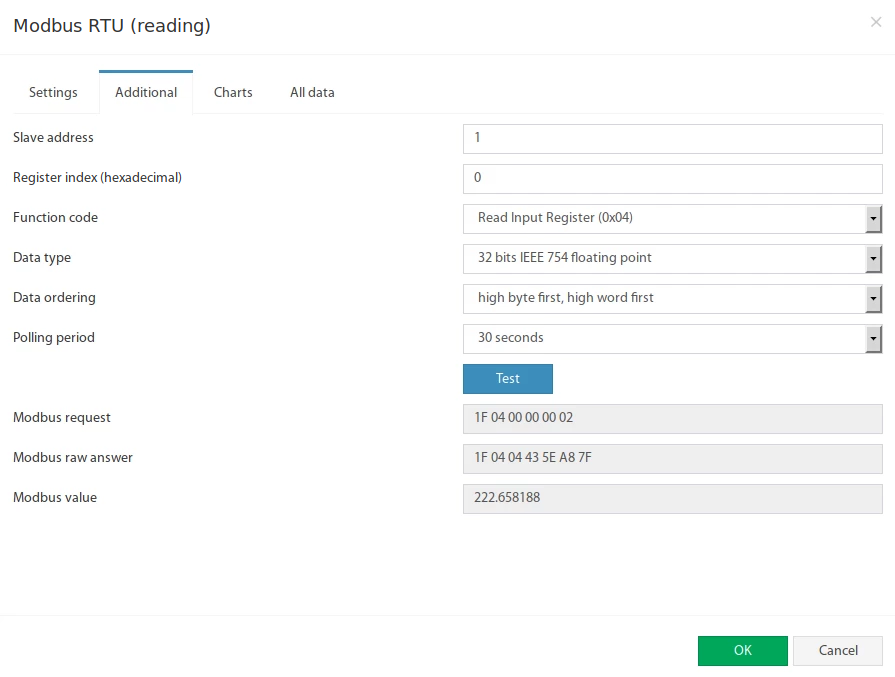
The Modbus RTU bus configuration is available in the "Additional" tab:
...
Fields in the form available for change:
# | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Slave address | Modbus RTU slave address of external equipment |
2 | Register index | Modbus protocol register start address in hexadecimal view, like 0F4A |
3 | Function code | The following functions are supported:
|
4 | Data type | Determines how to present the data:
|
5 | Data ordering | Determines byte order in Modbus protocol response message:
|
6 | Polling period | Defines the time of polling the sensor value. From 10 seconds to 5 minutes. |
The Test button allows you to make a test connection with a Modbus device. In additional fields, the bytes sequence of connection, data is displayed, in hexadecimal form. Modbus request - data of the sent request, without a checksum. Modbus raw answer - data of the received answer, without a checksum. Modbus value - contains the data value interpreted under the selected Data type.
...
Fields in the form available for change:
# | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | Name | Created element name |
2 | Slave address | Modbus RTU slave address of external equipment |
3 | Register index | Modbus protocol register start address in hexadecimal view, like 0F4A |
4 | Function code | The following functions are supported:
|
5 | Writing value | Decimal integer value that will be written in the specified register |
The Test button allows you to make a value entry immediately into the Modbus register. Now the Modbus RTU writing can be inserted as a THEN task in logic schemes:
...
...
For this example, we will be using the "Eastron SDM220-Modbus Single Phase Two Module DIN-rail Meter" as a slave Modbus device.
SDM220Modbus_protocol_V1.1.pdf
Let's create a "Modbus RTU" element for the input register "Active power", which is measured by SDM220.
Press add button " " inside the "Group tree" or "System tree" menu. Then choose "Modbus RTU". A Modbus element form will be opened:
...
Let's change values in the Setting tab:
# | Name | New Value |
|---|---|---|
1 | Name | We are adding the input register "Active power", so we write: Active power |
2 | User-defined type | Let's choose "power" for a nice icon of a meter. |
3 | Units of measurement | "Active power" is measured in Watts. so we write: Watts |
4 | Minimum value, Maximum value, Alarm, and warning levels | Define it according to Your needs |
7 | Hysteresis | Define it according to Your needs |
8 | Expression | x |
Now let's change the values in the Additional settings tab:
...
#
...
Name
...
Description
...
1
...
Slave address
on page 2 of SDM220ModbusEN.pdf it is stated in the table in row 16 that:
"How to find Modbus address. By default, it is 001"
But in our case it is different, a slave address has been manually altered. And, after following the procedure and navigating to slave address onscreen instruction, we find out that the Salve address for this device is currently set to 31 in our example. It is advised to have a slave address according to position in a Modbus chain. So if the sensor is currently 1st in a Modbus chain, set it to 1.
So we write 31.
...
2
...
Register index
on page 2 of SDM220Modbus_protocol_V1.1.pdf it is stated in the table that:
"Hi Byte = 00
+
Lo Byte = 0C"
So we write 000C
...
3
...
Function code
...
on page 2 of SDM220Modbus_protocol_V1.1.pdf it is stated that:
"Modbus Protocol function code 04 is used to access all parameters."
So we write:
0x04 - Read Input Registers
...
4
...
Data type
on page 1 of SDM220Modbus_protocol_V1.1.pdf it is stated that:
"The format for each byte in RTU mode is:
Coding System: 8-bit per byte
Data Format: 4 bytes (2 registers) per parameter.
Floating point format ( to IEEE 754)"
or
on page 2 it is stated that:
"the data used by the Eastron Digital meter is in 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point format."
So we write:
32 bits IEEE 754 floating point
...
5
...
Data ordering
on page 1 of SDM220Modbus_protocol_V1.1.pdf it is stated that:
"Most significant register first (Default). The default may be changed if
required -See Holding Register "Register Order" parameter."
So we write:
low byte first, low word first
Save the virtual Modbus element.
Now You can add the next virtual Modbus element using the register index for the same Eastron SDM220 Modbus slave. For example, Current, Apparent power, Reactive power, and so on.
...
Modbus configurations for tested sensors
See the article Modbus configuration for tested sensors